You love pizza, but what about your blood sugar levels? If you’re managing diabetes or just want to keep your energy steady, understanding how pizza affects your blood sugar is key.
Pizza isn’t just about carbs from the crust—its cheese and meats slow digestion, causing a tricky two-phase blood sugar response. This can make it hard to keep your levels stable. But don’t worry, you don’t have to give up your favorite slice.
You’ll learn simple tips to enjoy pizza without the blood sugar rollercoaster. Ready to find out how to make smarter pizza choices for your health? Keep reading!
Pizza And Blood Sugar Basics
Understanding how pizza affects blood sugar is important for many people. Pizza can raise blood sugar levels in two main ways. The carbohydrates in the crust and sauce cause a quick rise. Then, the fat and protein in cheese and meats slow digestion. This slow digestion can cause blood sugar to rise again hours later. This creates a two-phase blood sugar response that can be tricky to manage.
Knowing these basics helps with better meal planning. Choosing the right crust and toppings can reduce blood sugar spikes. Let’s break down how each part of pizza affects blood sugar.
Carbs In Crust And Sauce
Pizza crust usually contains refined flour. These carbs break down fast into sugar. This causes a quick rise in blood sugar after eating. The tomato sauce also adds some carbs, but less than the crust. Thick crusts and extra sauce mean more carbohydrates. Choosing thin or whole-grain crust lowers the carb load. This helps keep blood sugar steadier after meals.
Fat And Protein Effects
Cheese and meat toppings contain fat and protein. These nutrients slow down digestion. This means sugar enters the blood more slowly. After the initial spike from carbs, fat and protein cause a delayed blood sugar rise. This delayed effect can last for hours. It makes blood sugar levels harder to predict and control.
Two-phase Blood Sugar Response
Eating pizza triggers two phases of blood sugar change. First, carbs cause a fast increase. Then, fat and protein create a slower, prolonged rise. This two-phase response is a challenge for people with diabetes. Insulin dosing must consider both the early and late spikes. Managing portion size and topping choices can reduce these effects.

Credit: www.vively.com.au
Blood Sugar Levels After Pizza
Eating pizza can cause changes in blood sugar levels. The crust’s carbohydrates lead to a quick rise in glucose. Cheese and meats slow digestion and cause a delayed blood sugar increase. This two-phase effect can be hard to manage, especially for people with diabetes. Understanding how pizza affects blood sugar helps make better food choices.
Normal Blood Sugar Range
After eating, normal blood sugar usually stays below 140 mg/dL. For most adults without diabetes, blood sugar peaks within 1 to 2 hours. The body then brings levels back to normal. Staying within this range helps avoid fatigue and other health issues.
Impact On People With Diabetes
Pizza can cause large blood sugar swings in people with diabetes. The quick rise from the crust may spike glucose dangerously high. The fat and protein slow digestion, causing another rise hours later. This makes insulin dosing tricky and can lead to highs and lows. Monitoring blood sugar closely after pizza is important. Choosing the right crust and toppings helps reduce spikes.
Choosing The Right Pizza
Choosing the right pizza helps control blood sugar levels better. Not all pizzas affect your body the same way. The type of crust and toppings can change how your blood sugar reacts. Making smart choices can reduce spikes and keep you feeling good after eating.
Crust Options
Thin crust pizzas raise blood sugar less than thick crusts. Whole-grain crusts add fiber, which slows sugar absorption. Cauliflower or almond flour crusts have fewer carbs and suit blood sugar control. Avoid crusts made from refined white flour. They cause quick blood sugar spikes and less fullness.
Toppings To Favor
Vegetables add fiber and nutrients without many carbs. Choose peppers, spinach, mushrooms, and onions for your pizza. Lean proteins like grilled chicken or turkey help stabilize blood sugar. Cheese in moderation is fine but watch the amount. Fiber and protein slow digestion and lower sugar rises.
Toppings To Avoid
Processed meats like pepperoni and sausage contain fat and salt. They can raise blood sugar and increase insulin resistance. Extra cheese adds more fat, slowing digestion but also increasing calories. Avoid sugary sauces or honey drizzles. They add hidden sugars that spike blood sugar quickly.

Credit: www.glucosense.ai
Managing Portions And Pairings
Managing portions and pairings plays a key role in controlling blood sugar after eating pizza. Portion size affects how much carbohydrate enters your bloodstream at once. Pairing pizza with the right foods can slow sugar absorption and reduce spikes. Planning your meal helps maintain steady glucose levels and supports overall health.
Portion Control Tips
Start with one or two small slices instead of a large portion. Use a smaller plate to avoid overeating. Eat slowly to give your body time to signal fullness. Avoid second servings until you feel satisfied. Balance your pizza intake with other low-carb foods to keep blood sugar stable.
Best Side Dishes
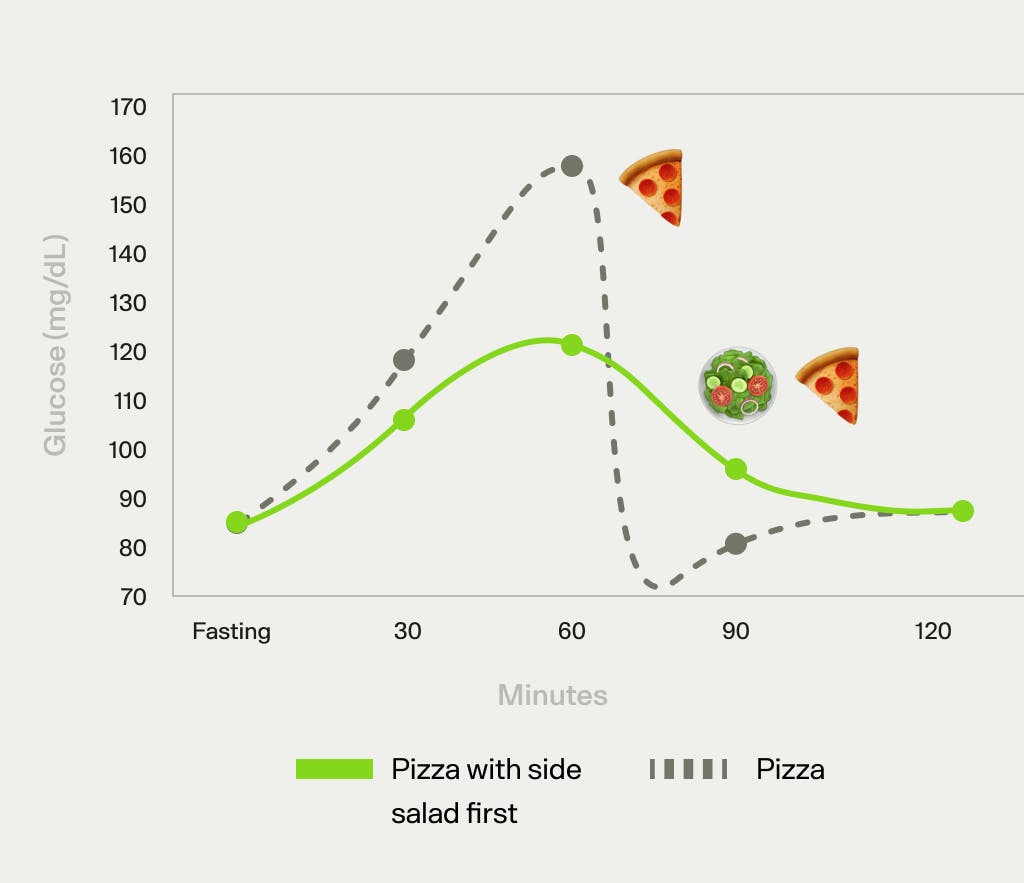
Choose side dishes rich in fiber and low in carbs. A green salad with olive oil dressing works well. Steamed or roasted non-starchy vegetables add nutrients without raising blood sugar. Avoid high-carb sides like fries or breadsticks. These choices help slow digestion and reduce blood sugar spikes.
Timing Your Meal
Eat pizza at times when you can be active afterward. Physical activity helps your body use glucose better. Avoid eating pizza late at night to prevent overnight blood sugar rises. Space your meals evenly throughout the day to keep levels steady. Timing can improve how your body handles the pizza’s carbs and fats.
Insulin And Blood Sugar Control
Controlling blood sugar after eating pizza can be tricky. Pizza has carbs that raise blood sugar quickly. Cheese and meats slow digestion, causing a late rise in blood sugar. This pattern makes insulin management complex for many people. Understanding how insulin works with pizza helps keep blood sugar steady.
Adjusting Insulin Doses
Insulin doses may need changes before and after pizza. The fast carbs in the crust cause a quick blood sugar rise. People often take insulin at mealtime to cover this spike. The fat and protein delay digestion and cause a second blood sugar rise later. Extra insulin may be needed hours after eating. Careful timing and dose adjustments help avoid highs and lows.
Delayed Blood Sugar Spikes
Pizza causes blood sugar to rise in two phases. The first spike happens soon after eating due to carbs. The second spike comes hours later from fat and protein slowing digestion. This delayed rise can last for several hours. It is harder to predict and control. Monitoring blood sugar frequently after pizza is important to catch late spikes.
Carb Counting Challenges
Counting carbs in pizza is not simple. Crust carbs are easy to estimate but toppings add complexity. Cheese and meats have little carbs but affect blood sugar by slowing digestion. This changes the timing of blood sugar rises. Many find it hard to match insulin with this mixed effect. Using carb counting with experience and blood sugar tracking improves control.
Benefits Of Leftover Pizza
Leftover pizza offers more than just convenience. Cooling pizza changes its starch structure. This change can benefit your blood sugar levels. Eating cold or reheated pizza may reduce its impact on blood sugar. This happens because of resistant starch, a type of fiber your body digests slowly. Resistant starch helps control blood sugar spikes and keeps you full longer.
Resistant Starch Formation
When pizza cools, some starch turns into resistant starch. Resistant starch resists digestion in the small intestine. It passes to the large intestine where good bacteria feed on it. This process improves gut health and helps regulate blood sugar. Cold pizza has more resistant starch than fresh, hot pizza. Reheating pizza does not fully remove resistant starch, so leftovers still offer benefits.
Reduced Blood Sugar Impact
Resistant starch slows down glucose absorption into the bloodstream. This slower absorption means blood sugar rises more gently after eating. Eating leftover pizza can cause smaller blood sugar spikes than fresh pizza. This is helpful for people managing diabetes or insulin resistance. Leftover pizza’s fat and protein also help slow digestion, reducing blood sugar impact further.
Practical Tips For Pizza Lovers
Enjoying pizza does not mean you must ignore your blood sugar health. Simple changes can help you enjoy pizza without large sugar spikes. Practical tips allow pizza lovers to make smarter choices and manage blood sugar effectively.
These tips include balancing your meal, watching your blood sugar closely, and choosing healthier pizza options. Each step helps keep your blood sugar steady and your pizza time joyful.
Balancing Meals
Pair pizza with fiber-rich foods like salads or steamed vegetables. Fiber slows sugar absorption and reduces blood sugar spikes. Avoid eating pizza alone or with sugary drinks. Adding protein and healthy fats to your meal also helps balance blood sugar levels.
Monitoring Blood Sugar
Check your blood sugar before and after eating pizza. This helps you understand how different pizzas affect your levels. Use this information to adjust portion sizes or meal timing. Tracking your levels regularly can prevent unexpected highs or lows.
Healthy Pizza Alternatives
Choose thin crusts made from whole grains or vegetables like cauliflower. Use low-fat cheese and lean protein toppings such as chicken or turkey. Load your pizza with plenty of vegetables to add fiber and nutrients. These swaps reduce carbs and fat, helping control blood sugar better.
Credit: www.veri.co
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Pizza Bad For Blood Sugar?
Pizza with refined crust and high-fat toppings can cause blood sugar spikes. Choose whole-grain crusts, veggies, and control portions to manage levels.
What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level After Eating Pizza?
A normal blood sugar level after eating pizza is below 140 mg/dL for most non-diabetic adults within two hours.
How Much Glucose Is In Pizza?
A typical slice of pizza contains about 3 grams of glucose. Carbs in the crust mainly cause blood sugar spikes.
Is Pizza Bad For Blood Sugar Control?
Pizza with refined crusts and high-fat toppings can cause blood sugar spikes. The carbs raise glucose quickly, while fat and protein delay digestion, creating a prolonged effect. Choosing whole-grain crusts and healthy toppings helps manage blood sugar better.
Conclusion
Pizza can cause both quick and delayed blood sugar rises. Choosing thin or whole-grain crusts helps reduce spikes. Adding vegetables and lean proteins balances the meal well. Watching portion sizes keeps your blood sugar steady. Pairing pizza with a salad slows sugar absorption.
People with diabetes may need to adjust insulin timing. Understanding pizza’s effects helps manage blood sugar better. Enjoy pizza wisely to maintain healthy levels and feel good.

As the author of the “Ultimate Pizza Guide: Recipes, Tips & Secrets Revealed,” I’m dedicated to sharing my love for pizza and empowering others to create delicious homemade pizzas with ease. Join me on a journey to uncover the secrets to perfecting your pizza game!


